Description
Hydrogen Fuel Cells will record strong growth by 2040
Favourable regulation, innovation and powertrain decarbonization strategies drive Hydrogen adoption
Hydrogen is a strong condidate to support the zero-emission strategies of automotive players, together with batteries.
We believe that Hydrogen has a crucial role in the electrification strategies of players in the new era of electrified mobility.
Today, the application of H2 as a transportation fuel is still in its infancy because of the high cost of production, challenges in handling and distributing and nascent refueling infrastructure network. Value chains can be complex and require cross-sector investment co‑ordination, which multiplies risks.
Despite the techno-commercial challenges, we expect a boost in the adoption of H2 Fuel Cell Mobility driven by:
- favourable government policy to support net-zero goals,
- innovation to lower the cost of storage and distribution; lower the cost of Green Hydrogen
- stronger player activities to adopt H2-ICE and Fuel Cells in cars and Heavy-Duty Trucks
Hydrogen Mobility has a Total Addressable Market (TAM) of $185 Billion by 2026, while Fuel cells have a TAM of $12 Billion.
In this report we examine these three drivers in detail. We also assess the opportunities in Heavy-Duty Trucks, Hydrogen-Internal Combustion Engines and Green H2.
- Hydrogen as a fuel. In December 2023, Amazon partnered with Plug Power to produce their own H2 on-site for their fullfilment centers.
- H2 is particularly suitable for zero-emission trucks carrying heavy goods over long distances because of faster charging and longer range compared to battery-electric trucks.
- Innovation in Fuel cells: High Temperature PEMs and Solid Oxide fuel cell could emerge as a reliable power source for automotive in future
- H2-ICE could become an interim electrification strategy for players to extend the lifecycle of existing ICE assets
- The drop in cost of Green H2, i.e. produced by renewables, could enable wider adoption to support cleaner vehicle manufacturing
Hydrogen adoption in cars, Commercial Vehicles and trucks is still in its infancy
The adoption of H2 Fuel Cell (FC) technology in vehicles is still in early stages, with 72,000 Fuel Cell vehicles sold globally in 2022, according to the IEA.
Korea leads global FCEV car sales, followed by the U.S, whereas China accounts for 95% of the global fuel cell truck fleet and almost 85% of the global fuel cell bus fleet.
The penetration of FCs and batteries is still nascent in CVs and Trucks. In 2022, circa 66,000 electric buses and 60,000 medium- and heavy-duty trucks were sold globally, accounting for 4.5% of all bus sales and 1.2% of truck sales worldwide.
In contrast, in Norway, the country with the highest penetration of EVs, Battery Electric Vehicles accounted for more than 17% of all light-duty vehicles on the road in 2022. In Norway, 79.3% of new cars sold in 2022 were battery BEVs.
H2 refueling infrastructure amounted to 1,020 stations in 2022. Infrastructure networks continue to be developed in areas where vehicle manufacturers, providers, and governments share an interest in paving the way for greater fuel cell vehicle deployment.
We are experiencing a sharp shift to zero-emission technologies from the automotive industry which now focuses on Hydrogen for Commercial vehicles and Heavy-Duty trucks to meet sustainability and zero-emission goals.
Innovation to solve the challenges of Hydrogen is gaining pace
Platinum is a major contributor to the high cost of FCVs. Platinum is expensive which increases the initial cost of fuel cell production. Replacing it with another material which gives the same effectiveness for oxidation-reduction reaction that of Pt is difficult.
Extensive research over the past several decades was focused on developing alternative catalysts, including non-noble metal catalysts. These electro catalysts include noble metals and alloys, carbon materials, quinone and derivatives, transition metal macrocyclic compounds, transition metal chalcogenides, and transition metal carbides.
Over the past year, research work to cut down platinum costs has gained momentum. Recent catalyst developments are key to the future of fuel cell technology, and the large-scale commercialization of clean electric power for transportation, as they:
- Reduce fuel cell costs, by reducing the use of precious metals
- Improve durability through innovative catalyst layer designs
- Increase robustness to a range of operating conditions
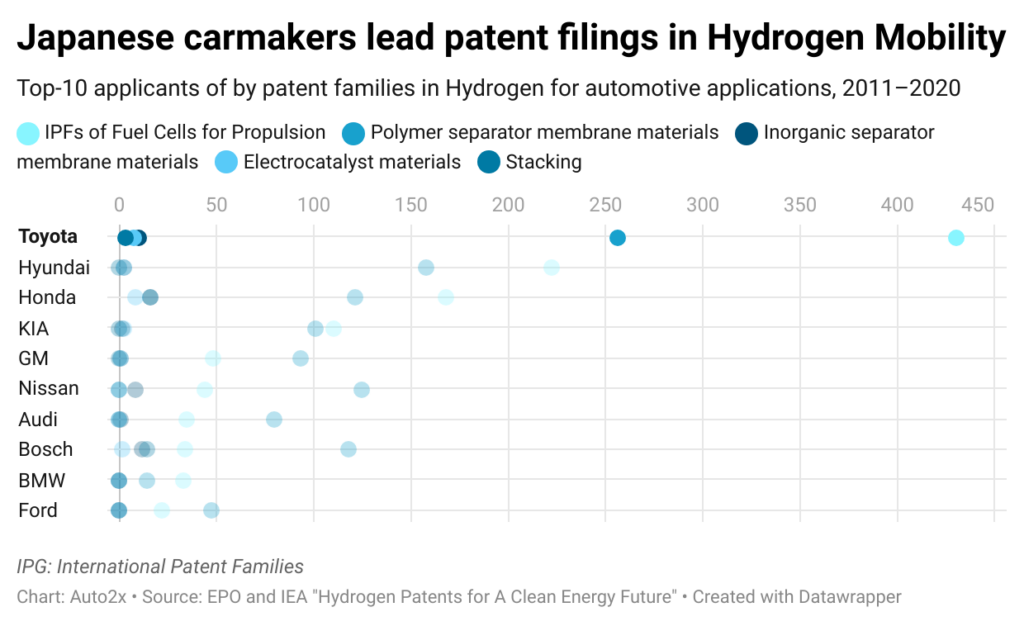
Toyota, Honda and Hyundai top Hydrogen patent filings
Patent filing publications can provide strong signals of innovation and help scout for new opportunities, technologies or strategies.
A joint study by the European Patent Office and the International Energy Agency (IEA) on Hydrogen Patents in January 2o23 found that Japanese carmakers are among the top innovators in Automotive.
Europe and Japan lead patents filings in this domain while the U.S is losing ground, finds EPO-IEA study.
Favourable policy for net-zero and energy security will lead to new Hydrogen Hubs
Favourable policy in China, Europe and Japan will lead to the development of new Hydrogen hubs and benefit strategies for fleet decarbonization, especially for heavy-duty trucks
China has recently extended the incentives for NEVs (New Energy Vehicles) but has also shown commitment to Hydrogen mobility through incentives for FCVs. NEV sales in China, which include BEV, PHEV and FCV, rose to 1.25 million. NEV sales have recorded a CAGR of 59.8% between 2014 & 2020.
Alongside renewable electrification and a more efficient and circular use of resources – as set out in the Energy Sector Integration Strategy – large-scale deployment of clean hydrogen at a fast pace is key for the EU to achieve its high climate ambitions. The European Union has aggressively committed to putting the necessary infrastructure in place for Green H2.
In September 2020, France presented the national hydrogen strategy with a plan to provide an investment of €7.2 billion by 2030 and a hydrogen production capacity of 6.5 GW by 2030.
France announced its Hydrogen Deployment Plan for Energy Transition in June 2018, the targets of which include 20-40% low-carbon hydrogen use in industrial applications of hydrogen, and a reduction in electrolysis cost to EUR 2-3/kg by 2028.
In 2020, Germany’s National Hydrogen Strategy earmarked $8.2 Billion for investments in new business and research around green hydrogen and $2.3 Billion to support international partnerships and development.
Japan and South Korea are expected to be pivotal in advancing the fuel cell electric vehicle technology, as Toyota and Hyundai-Kia claim to become the global leaders in fuel cell technology.
The opportunity for Hydrogen in Commercial Vehicles and Trucks
Long-haul truck applications contribute the large amount of the CO2 emissions from CVs. Stricter emission norms push for a solution.
The EC states that Fuel-Cell trucks can become cost-competitive by 2027, if hydrogen drops to €6/kg.
In Europe, for the first time, the commercial vehicle industry made a pledge that by 2040 all new trucks sold need to be fossil free in order to reach Europe’s carbon-neutrality goal by 2050.
- In November 2020, Toyota, Hyundai, Honda, HYZON Motors, Ballard, Michelin, Total, Engie, Shell, and BMW Group committed to adopting hydrogen trucks.
- In December 2020, Daimler, Scania, Man, Volvo, Daf, Iveco, Ford agreed to the transition to zero-emission road freight transport. 2021 saw seven collaborations in Hydrogen Trucks between Honda-Isuzu, Faurecia-Hyundai, Daimler-Volvo, and Toyota-Hin, among others.
Players explore Hydrogen-Internal Combustion Engine
H2-ICE as a potential solution for zero emission mobility to convert large fleet of ICEs into green vehicles. These vehicles tend to fall in a middle ground between the higher efficiency hydrogen fuel cell vehicles and the standard gasoline ICE vehicles.
Currently, for H2-ICE’s to qualify as zero-CO2 emissions solutions in Europe, they must not produce more than 1g CO2/kWh.
Toyota is making big bets not only to save the ICE but to replace EVs.
The cost of Green Hydrogen will drop to make clean production sustainable
Most hydrogen extracted today is from natural gas (“Grey”) in a process that produces carbon emissions. Green hydrogen requires a large amount of renewable electricity to produce.
The cost of green hydrogen is expected to see dramatic cost reductions this decade as the cost of renewable energy and electrolysers fall, to the point where it can compete with grey even without a carbon price according to Energy Transitions Commission.
Increased demand could reduce the cost of electrolysis. Coupled with falling renewable energy costs, green H2 could fall to $1.7/kg by 2050 and possibly sub-$1/kg, making it competitive with natural gas.
Emerging Hydrogen Start-ups to watch
Three innovative start-ups working on Hydrogen & Fuel Cells for Automotive Applications
| Domain | Company | Technology | Key differentiation |
| Green Hydrogen | Advanced Ionics | Symbiotic ™ Electrolyzers | Advanced Ionics has developed an electrolyser that runs at temperatures below 650 C and it is reportedly able to produce hydrogen for <$0.85/kg. |
| Fuel Cells | GenCell | Alkaline fuel cell (AFC) | Offers alkaline fuel cell (AFC) technology, the only fuel cell technology with the chemistry and robustness that can utilize hydrogen produced from cracking ammonia, according to the company |
| Advent Technologies | HT-PEM Fuel Cell | HT – PEM (High Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane) that can use any fuels such as Hydrogen, methanol, natural gas, ethanol, other alcoholic fuels |
Start-up funding in automotive
Heavy Duty Vehicles (HDV) play a crucial role on commerce and trade, but diesel dominates their powertrain, with 90% penetration in new sales in China.
Electrification and autonomous driving could play an important role in the decarbonization of global Heavy-Duty transportation and logistics.
Start-up funding is heating up, especially in China, who is promoting clean trucks with a series of policies.
DeepWay, a Chinese manufacturer of the Heavy-Duty Autonomous Truck Xingtu, raised $110 Million (CNY 770 Million) in a Series A Round in March 2023. The company was established in 2020 by Baidu and Lion Bridge. DeepWay is working with Weiqiao Pioneering, the world’s largest aluminium producer, to use smart e-trucks in closed-loop deliveries, but they are also exploring other use cases.
Foripower, a Chinese start-up focused on new energy vehicle power supply and domestic H2 fuel cells, raised funding in Q1 2023.
In April 2023, Green Hydrogen Company Ohmium closed $250 Million Series C Fundraise Led by TPG Rise Climate.